

Whenever you boot your computer, you’ll have the ability to choose between Mac OS X and Linux on the rEFInd boot manager screen.ĭepending on your Mac, some hardware components may not work perfectly on Linux. The installation process should otherwise be normal. Be sure to select the “Install Ubuntu alongside Mac OS X” option instead of overwriting your Mac OS X system with Ubuntu.
#How to get ubuntu on a mac hard drive install
On Ubuntu, launch the Install Ubuntu application from the desktop and install Ubuntu as you normally would. Launch your Linux distribution’s installer and go through the installation process. Drag and drop the handle on the partition volume or enter a final size for the partition and click Partition to partition it. Ubuntu’s system requirements say it requires at least 5 GB of space, but something like 20 GB is much more reasonable. How much space you want for Linux is up to you. Shrink the current Mac OS X partition to make space for your Linux system. RELATED: Beginner Geek: Hard Disk Partitions Explained
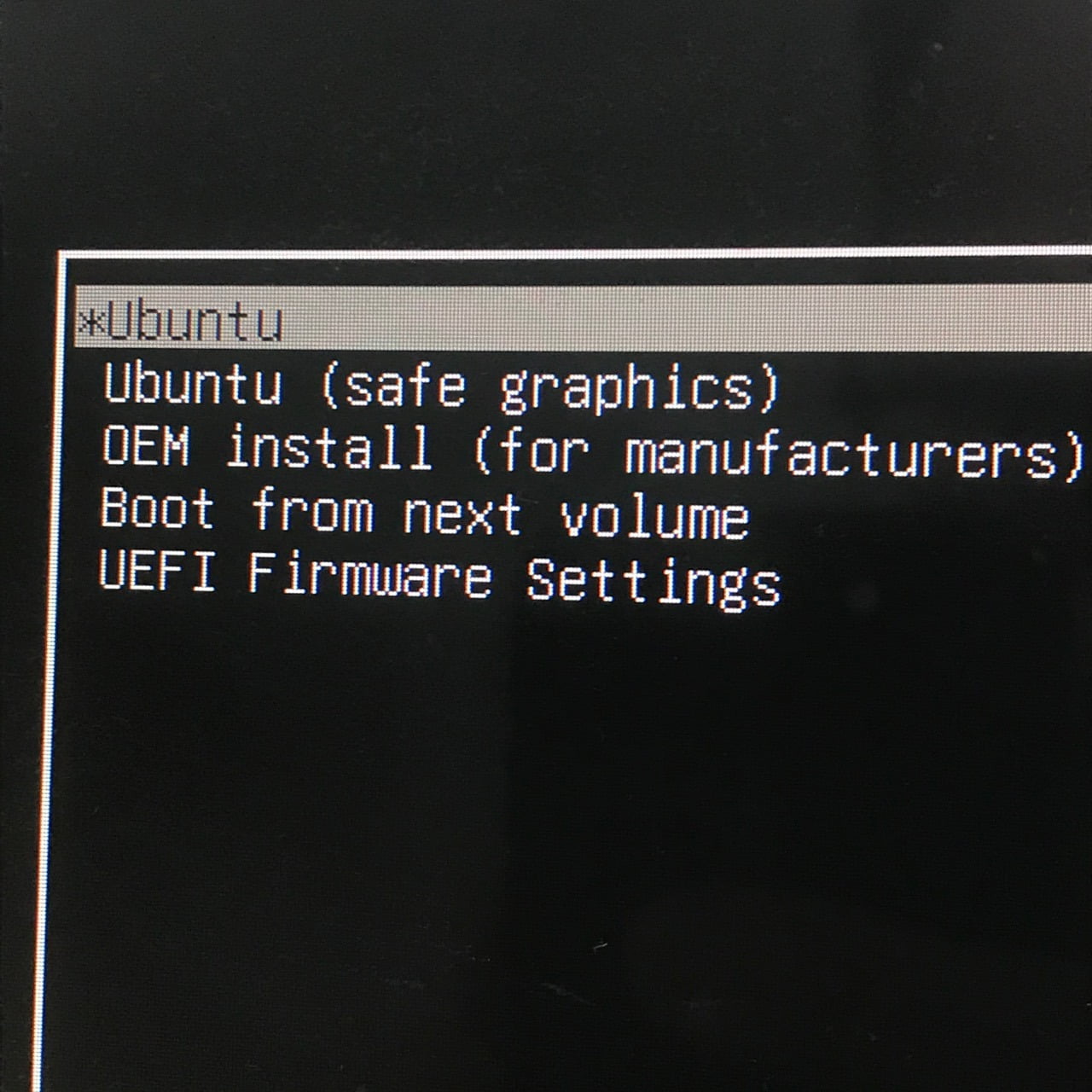
Select your Mac’s hard drive in the list on the left and select Partition on the right. From within Mac OS X, press Command + Space, type Disk Utility, and press Enter to open the Disk Utility. You’ll now need to resize your Mac OS X system partition to make room for your Linux distribution of choice. You should see the rEFInd boot manager screen. Shut down your Mac - a full shut down, not a restart - and boot it back up again. Drag and drop the install.sh file from the downloaded zip file into the terminal window and press Enter to run it. Open a Terminal window by pressing Command + Space and, typing Terminal, and pressing Enter. Full-disk encryption causes problems with rEFIt, so you’ll need to disable full-disk encryption or do some extra work before installing rEFInd.įirst, visit the rEFInd page on SourceForge and click the Download button to download the latest refind-bin-.zip file.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
